Lobaplatin for Injection
- FOB Price:Get Latest Price >
- Min.Order:1 Vial(s)
- Payment Terms:T/T , Others
- Favorite
Business Type:Manufacturer
Country/Region:China
Ddu Verified
HOT Rank


Hainan Changan International Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
We are professional supplier of Lobaplatin for Injection(50mg),Lobaplatin for Injection(10mg).
Business Type:Manufacturer
Country/Region:China
Ddu Verified
HOT Rank

[Ingredient]
The product is mainly lobaplatin.
Chemical name: 1,2-diamminomethyl-cyclobutane-platinum(II)-lactate
Chemical formula:
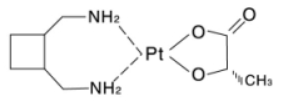
Molecular formula: C9H18N2O3Pt
Molecular weight: 397.34
[Description]
White lyophilized powder
[Administration and Dosage]
Before administration, use 5ml water for injection to dissolve. Solution shall be administered within 4 hours (storage temperature: 2~8℃). Intravenous injection shall be 50mg/m2 one-time according to body surface area. Next administration is recommended when blood toxicity or other clinical adverse reactions are gone. Recommended interval is 3 weeks. In case the adverse reactions go away slowly, interval may be longer. Administration duration: treatment duration depends on tumor reaction. At least 2 courses of treatment are necessary. In case the tumor shrinks, treatment may proceed to 6 courses of treatment in total.
[Adverse Effects]
1. Blood toxicity: among dose-limiting toxicities of lobaplatin, thrombocytopenia is the strongest. Almost 26.9% of patients with solid tumor have thrombocyte count lower than 50,000/mm3. Among patients with ovarian cancer that have gone through large-dose chemotherapy, frequency of thrombocytopenia reaches 75%. thrombocyte count starts to drop two weeks (14 days) after administration of lobaplatin and goes back to 100,000/mm3 after dropping for a week. Among 15% of patients (the percentage reaches 32.5% among patients with ovarian cancer that have gone through much chemotherapy), white blood cell count is as low as 2000/mm3. Change in blood routine examination results are reversible, but may cause secondary side effects, such as thrombocytopenia causing hemorrhage and leukopenia causing infection.
2. Gastrointestinal toxicity: 34.3% of patients vomit, yet only 6.7% of them vomit seriously; 14.8% patients have nausea. Preventative antiemetic is recommended. 3.5% patients have diarrhea.
3. Neurotoxicity: 1.3% of patients have abnormal feelings. Nerve diseases, neuralgia, ototoxicity, derangement, visual abnormality, etc. only take place in less than 0.5% of patients.
4. Renal toxicity: in the administration of lobaplatin, most patients need no large-quantity transfusion or/and forced diuresis. Abnormality in renal function is rare. Patients with anorexia have insufficient liquid intake after administration of lobaplatin. Serious vomit may cause toxicity renal function to fail.
5. Hepatotoxicity: after administration of lobaplatin, light reversibility is occasional. SAST and SALT have a rise, which may be caused by liver transfer, yet the causality with lobaplatin cannot be ruled out.
6. Electrolyte change: electrolyte change does not constitute a side effect of lobaplatin.
7. Anaphylactic reaction: around 1.9% of patients have anaphylactic reactions (such as anaphylactoid purpura with rash, skin flush, skin reaction), which is common in patients with ovarian cancer that have received large amount of platinum compound therapy in the past. There is no such side effect in case of CML.
8. Other side effects: no chronic carcinogenicity test has been done. Compounds with mechanism similar to lobaplatin are malformation-induced and carcinogenic. Therefore, while using lobaplatin for therapy, risk of secondary tumor cannot be excluded. Side effects of lobaplatin regarding male fertility cannot be completely excluded.
[Contraindication]
Myelosuppression, dysfunction in clotting mechanism (which may cause hemorrhage or potential for hemorrhage) and damage in renal functions. Allergic reactions to platinum compound.
[Use during pregnancy and lactation]
Forbidden during pregnancy and lactation. Women with fertility shall avoid pregnancy during lobaplatin therapy and within 6 months upon termination of lobaplatin therapy.
[Drug Interactions]
In case lobaplatin is administered along with other myelosuppression drugs, marrow toxicity may increase.
[Pharmacology & Toxicity]
1. Pharmacology: with alkylate effects, one kind of alkalating agents (in a broad sense). The product has obvious cytotoxic effects on cell strains of multiple kinds of animal and human tumor. Tumor suppression effects are similar or stronger than those of cisplatin. The product has cell strains resistant to cisplatin and certain cytotoxic effects.
2. Toxicity: chronic toxicity test on rats and dogs demonstrates similar toxicity as that of carboplatin. Main toxicity is suppression in bone marrow hemopoiesis.
3. Renal toxicity is relatively low. Mutagenic effects are shown in both vivo and vitro test. Carcinogenicity test has not been done yet, but these kinds of alkylating agents are all potentially malformation-induced and carcinogenic.
[Pharmacokinetics]
After intravenous injection, blood medicinal concentration-time curve of free platinum in serum is basically the same as complete lobaplatin. In blood circulation, there are no or little metabolites. Two stereoisomer curves of lobaplatin are
completely the same. Concentration-time curve for total platinum and free platinum in the serum of administered patients is similar within 1 hour. After 11 hours, in blood circulation, 25% lobaplatin concentration and serum protein combines.
Terminal half-life (t1/2) of free platinum is 131 ± 15min. Total platinum is 6.8 ± 4.3 days. Standardized area under curve (AUC) of free platinum (50mg/m2) is (13.9±1.8) min · m2/L. Standardized average plasma clearance of free platinum (1.73m2) is approximately (125±14) ml/min. Standardized average plasma clearance of total platinum is (34±11) ml/min. Average volume of distribution for free platinum is (0.28±0.51) L/kg, for total platinum is (4.8±2.61) L/kg. The product is mainly discharged through kidney.